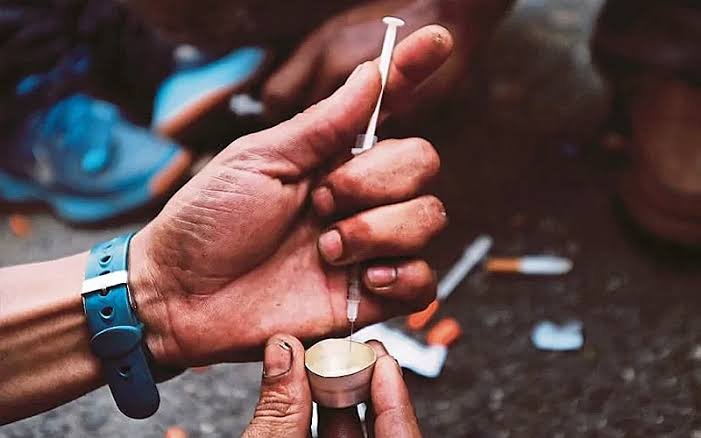
In a state lauded for its literacy and development, Kerala now faces an unimaginable crisis – youngsters are becoming victims of drug addiction. The harsh reality, revealed in a recent article titled “How Drugs are Trapping KG Kids” in the Times of India ( March 21, 2025), shows that what most citizens know about drug addiction in Kerala is merely the tip of a terrifying iceberg.
This article has revealed the devastating reality of drug addiction among Kerala’s children. The investigation by Disney Tom uncovered that children as young as five years old, still in kindergarten, are being lured into substance abuse. What began as childhood curiosity ends in full-blown addiction, with rehabilitation centers across the state reporting alarming statistics.
According to the report, a study of 210 students who underwent rehabilitation found that 70% were introduced to drugs as early as Class 3. At Samrudha Care Centre in Kottayam, counselors treat children who started using substances like hashish oil in kindergarten. The article details how drug cartels strategically target schoolchildren, offering the first dose for free, then trapping them in dependency and debt that many can only escape by becoming sellers themselves.
Most troubling is the expansion of this crisis to primary schools and the increasing number of schoolgirls seeking treatment. The article notes the high prices drugs command in Kerala—MDMA fetching ₹25,000 per gram and marijuana ₹25,000 per kilogram—creating powerful economic incentives for traffickers to target the young and vulnerable.While authorities like the Thrissur rural police have launched initiatives such as “Navajeevan” to support those battling addiction, more comprehensive solutions are urgently needed.
Here are some key solutions to help Kerala effectively combat its drug crisis:
1. Strengthening Early Education and Awareness
Schools must implement age-appropriate drug education starting in kindergarten. Rather than using fear tactics, programs should focus on developing critical thinking skills and resistance strategies. Children should be taught to recognize potentially dangerous situations and substances from an early age.
2. Empowering Parents with Knowledge
Parents need specialized training to identify early warning signs of drug experimentation. Schools and community centers should offer regular workshops teaching parents to recognize subtle behavioral changes, physical symptoms, and concealment techniques used by children using drugs. These sessions should normalize seeking help rather than perpetuating stigma. Moreover strengthen Parent-Teacher Associations (PTAs) to facilitate communication between parents and teachers, enabling early identification of at-risk children.
3. Creating Safe Reporting Mechanisms
Anonymous reporting systems should be established in schools and communities where children can safely report drug-related activities without fear of retaliation. These systems must be coupled with immediate protective measures for those who come forward.
4. Expanding Mental Health Support in Schools
Every school should have trained counselors capable of identifying at-risk children and providing early intervention. Regular mental health check-ins should become as routine as physical health examinations, with special attention to children showing signs of behavioral changes.
5. Strengthening Community Surveillance
Neighbourhood watch programs specifically focused on identifying drug-related activities near schools should be established. Community members should be trained to recognize suspicious behavior and report it to authorities through dedicated helplines.
6. Rehabilitation Focused on Youth
Kerala needs specialized rehabilitation facilities designed specifically for young children, with programs that address their unique developmental needs and psychological vulnerabilities. These centers should incorporate educational continuity to ensure children don’t fall behind academically.
7. Disrupting Supply Chains
Law enforcement must intensify efforts to identify and dismantle supply chains targeting schools. Special investigative units should focus exclusively on tracking how drugs enter school environments.
8. Utilising Technology
Schools should explore using advanced technologies like AI-powered surveillance systems in vulnerable areas around campuses to identify and prevent drug-related activities before they reach children.
9. Cross-Sector Collaboration
Healthcare providers, educators, law enforcement, social workers, and parents must collaborate through formal networks that share information and coordinate responses. Regular case conferences should review intervention strategies for individual children and identify systemic vulnerabilities.
10. Developing a State-Level Action Plan
Develop a comprehensive state-level action plan to address drug abuse among children and adolescents, incorporating the solutions mentioned above and involving all stakeholders
The crisis demands immediate, coordinated action. While public awareness is important, it’s merely the beginning. The Government of Kerala must acknowledge its critical role in addressing this crisis and take concrete, sustainable steps to protect children’s futures. It is the government’s responsibility to ensure that its youngest citizens grow up free from the devastating grip of addiction. The state’s reputation for high literacy and human development now faces its greatest challenge, and it is imperative that the government rises to this challenge.
The people of Kerala expect nothing less than a comprehensive, well-funded, and multi-faceted approach to tackling this crisis. The Government of Kerala must act now to prevent further devastation and safeguard the future of its children.